Causes of Poverty
Poverty is driven by a variety of complex factors. One of the primary causes is the lack of access to quality education, which limits job opportunities and earning potential. Unemployment and underemployment also play significant roles, leaving individuals without sufficient income to meet basic needs. Social exclusion, discrimination, and poor governance further perpetuate poverty by creating barriers to economic participation. Economic instability, armed conflicts, and natural disasters can devastate communities, making recovery difficult and perpetuating a cycle of poverty. Additionally, inadequate healthcare, poor infrastructure, and limited access to resources such as clean water and nutritious food exacerbate the problem, leading to poor health outcomes and reduced quality of life. Corruption and the unequal distribution of wealth also contribute to the persistence of poverty, making it harder for disadvantaged groups to improve their living conditions.
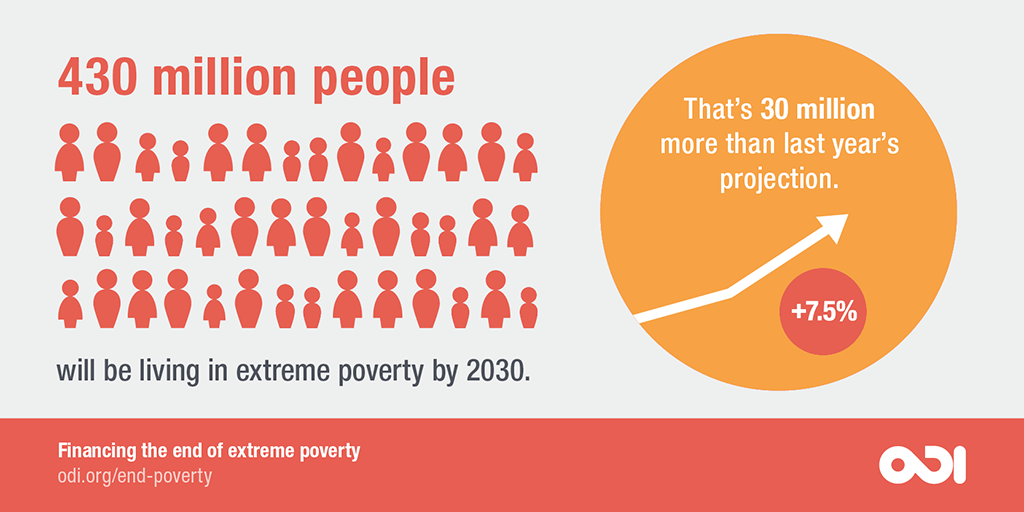
Life in Poverty
Living in poverty means facing daily struggles to secure basic necessities such as food, shelter, and healthcare. Individuals and families often live in overcrowded and unsafe housing conditions, with limited access to clean water and sanitation facilities. Malnutrition is common, particularly among children, leading to long-term health problems and hindered development. Educational opportunities are scarce, resulting in low literacy rates and limited future prospects. The constant stress of financial insecurity affects mental health, leading to higher rates of anxiety and depression. Social stigma and exclusion further marginalize those living in poverty, making it difficult to access support services and opportunities for improvement. The lack of resources and opportunities creates a cycle of poverty that is difficult to break, trapping generations in a state of deprivation and hardship.
Effects
Poverty has far-reaching effects on individuals, communities, and nations. On an individual level, it leads to poor health, malnutrition, and limited access to education, resulting in reduced life expectancy and lower quality of life. Communities affected by poverty often experience higher crime rates, social unrest, and weakened social cohesion. Economically, poverty limits productivity and economic growth, as a significant portion of the population is unable to contribute fully to the economy. Nations with high poverty rates face challenges in achieving sustainable development, as resources are stretched thin and investment in infrastructure, education, and healthcare is limited. The social fabric of these nations is often strained, leading to increased inequality and social tensions. Globally, poverty contributes to migration and displacement, as individuals seek better opportunities and living conditions elsewhere. Addressing poverty requires comprehensive strategies that encompass economic, social, and political dimensions to create inclusive and sustainable development.
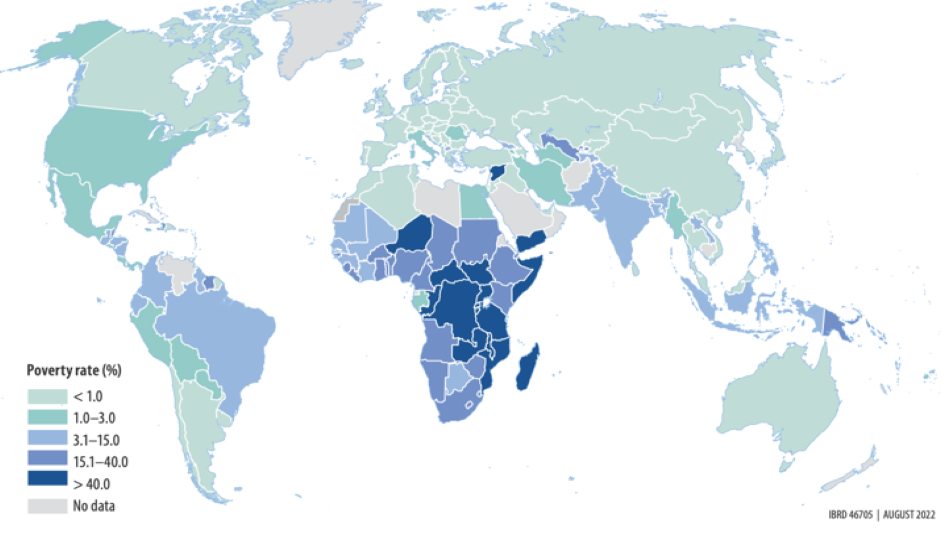
Impact on Communities
Communities impacted by poverty face numerous challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, poor educational facilities, and limited access to healthcare. This creates a cycle where poverty perpetuates itself, as future generations grow up without the tools needed to break free from deprivation. High unemployment rates and underemployment are common, leading to economic stagnation and a lack of opportunities for upward mobility. Social services are often insufficient, and support systems for vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and disabled, are lacking. Crime rates tend to be higher in impoverished communities, as individuals resort to illegal activities out of desperation. Social cohesion is weakened, leading to fragmentation and a lack of community solidarity. Addressing these issues requires targeted interventions that focus on improving infrastructure, providing quality education, enhancing healthcare services, and creating economic opportunities to uplift communities from poverty.
Solutions
Addressing poverty requires a multifaceted approach that includes economic, social, and political strategies. Economic measures include creating job opportunities, promoting fair wages, and supporting small businesses to stimulate economic growth. Social strategies involve improving access to quality education, healthcare, and social services to enhance human capital and well-being. Political solutions include implementing policies that promote social equity, reducing corruption, and ensuring good governance. International cooperation and aid are also essential in supporting poverty reduction efforts in developing countries. Additionally, empowering individuals and communities through capacity-building initiatives and promoting inclusive development can create sustainable pathways out of poverty. Addressing the root causes of poverty, such as inequality and social exclusion, is crucial for achieving long-term poverty reduction and improving the quality of life for all.

Empowering Communities
Empowering communities to take charge of their development is a key strategy in addressing poverty. This involves providing education and training to build skills and knowledge, promoting entrepreneurship, and supporting community-led initiatives. Access to microfinance and credit can help individuals start small businesses and improve their economic situation. Community engagement and participation in decision-making processes ensure that development efforts are tailored to the specific needs and priorities of the community. Social protection programs, such as cash transfers and food assistance, provide immediate relief and support to vulnerable populations. By fostering a sense of ownership and agency, communities can work together to create sustainable solutions to poverty and improve their overall quality of life.